Basic Policy on Internal Controls and Compliance System
We comply with laws, regulations, and contracts, and conduct appropriate transactions under fair and free competition.
- We treat all business partners fairly and equitably, and conduct transactions under appropriate conditions.
- We comply with laws such as the Act on Prohibition of Private Monopolization and Maintenance of Fair Trade, the Unfair Competition Prevention Act, the Act against Delay in Payment of Subcontract Proceeds, Etc. to Subcontractors, conduct transactions in accordance with sound business practices and social conventions. We do not give or receive profits that are inappropriate under the law or social conventions.
- We comply with the Patent Act, Copyright Act, other laws and regulations related to intellectual property rights, and company regulations. We strive to acquire, protect, and utilize our intellectual property rights, and respect the legitimate intellectual property rights of third parties.
- We comply with laws related to export control in the countries and regions in which we operate. We do not engage in transactions of export-controlled goods and technologies that may interfere with the maintenance of international peace and security. We also ensure that conflict minerals are not used.
- We completely sever relationships with anti-social forces and groups that threaten the order and safety of civil society, not only in our company but also in our supply chain.
- We maintain sound and normal relationships with politicians, political organizations, government agencies, etc.
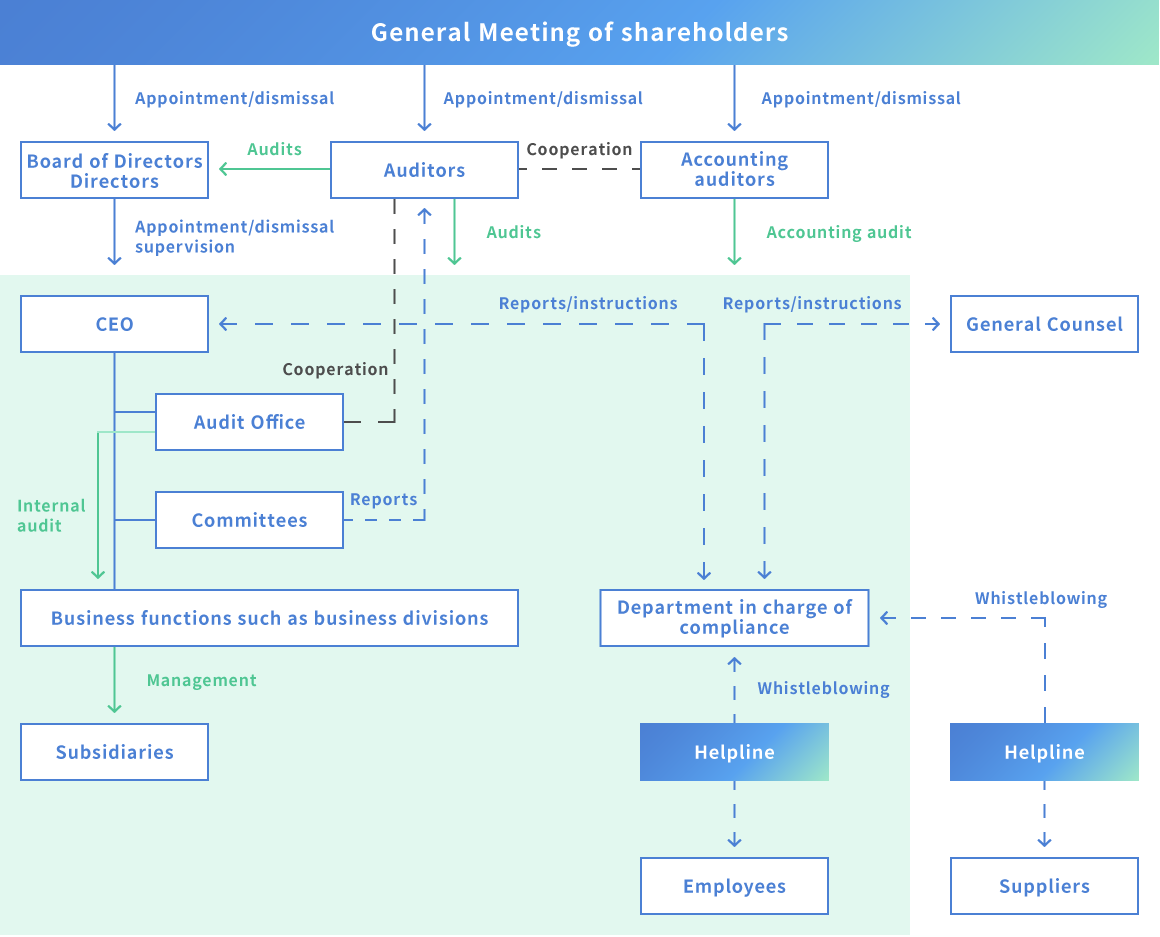
Corporate Governance System Diagram
Basic Internal Control Policy
We recognize that it is the responsibility of the Board of Directors and management to adopt a basic internal control policy at the Board of Directors and maintain and operate a solid internal control system, and have established an internal control system. Its purpose is to:
- Business efficiency and results (profitability, performance and asset preservation)
- Reliability of financial reporting
- Submission of reasonable assurance grounds for achieving compliance
In order to increase the effectiveness of internal controls, audits are conducted by auditors, accounting auditors, and the Audit Office.
Honest and Ethical Corporate Activities
Our basic policy is to comply with the laws, regulations, and social norms of the countries and regions in which we operate, and to conduct our business activities faithfully and ethically.
Handling of Information
We properly protect and manage company information, etc., and conduct appropriate communication and information disclosure to gain the correct understanding and trust from all stakeholders.
- We properly handle trade secrets and personal information of our company and third parties, and take appropriate measures to prevent inappropriate disclosure, leakage, use, and falsification.
- We do not improperly collect, disclose, leak, or use trade secrets or personal information of our company or third parties, whether during employment or after retirement.
- We fairly disclose company information such as management policies, business activities, financial reports, and incidents based on objective facts, and gain the correct understanding and trust from customers, shareholders, business partners, local communities, etc.
- We do not engage in insider trading such as buying and selling securities based on undisclosed company information.
Information Security Education
In order to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information assets of our company and other affiliated companies, we have established items which are standards for the handling of information assets. We also periodically hold information security education throughout the company, and strive to ensure proper information management.
Export Control
We do not engage in transactions that may threaten international peace and security. Furthermore, in order to comply with relevant domestic and foreign laws and regulations (for example, the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act), we have established export control regulations and established an export control system, and conduct applicability judgments and transaction screenings for exports of goods and provision of services.
Additionally, by implementing internal audits and export control education for promoted employees, we are making company-wide efforts to achieve appropriate security export controls.
Risk Management
About Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
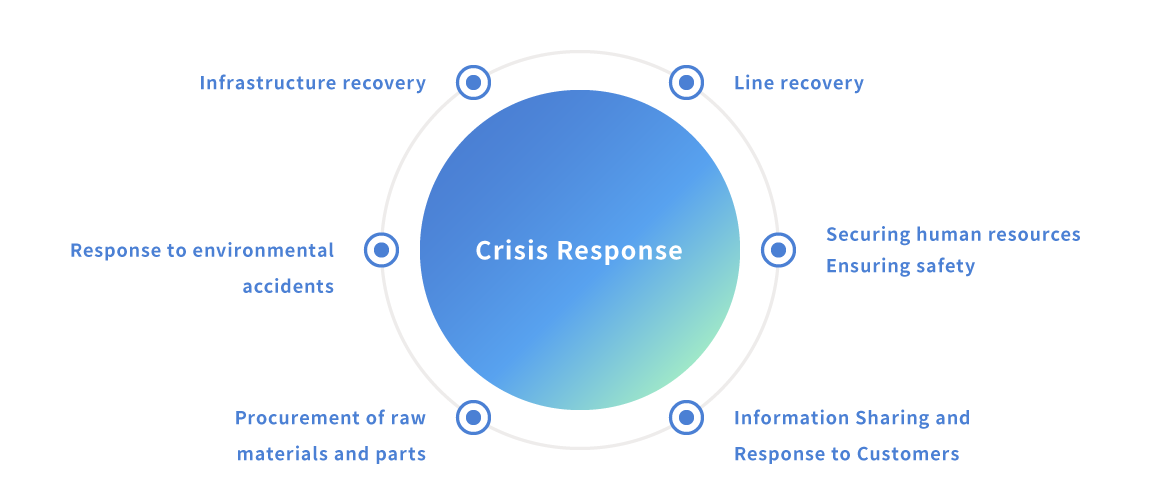
Our company envisions business continuity crises for various risks. In the event that a risk occurs, in order to minimize the damage suffered by all related parties (including the local community), we have established an organizational structure for response and role-sharing procedures in our Business Continuity Plan.
Basic Policy
Purpose of BCP/Scope of application
Purpose
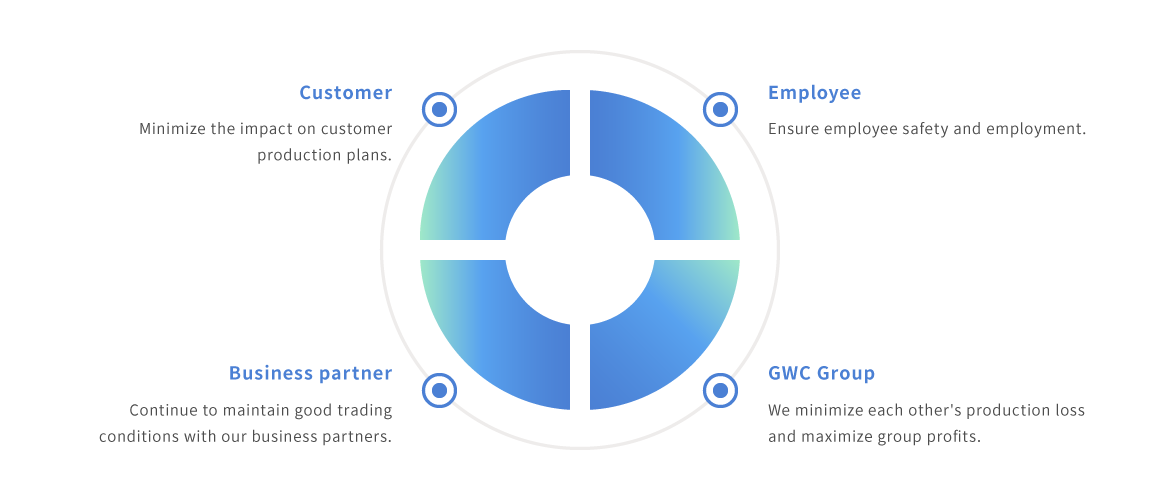
We have established an organizational structure, division of roles, and procedures to deal with business continuity crises at our company.
In the event of a crisis, we aim to minimize the damage suffered by customers, business partners, our company, the GWC Group, and employees.
Scope of Application
We define a "business continuity crisis" as a situation in which core business operations are expected to be interrupted; for example, a situation in which operations are suspended for more than two weeks. Examples of crises include natural disasters such as earthquakes, fires, storms and floods, accidents, crimes, and disputes. We issue BCP for these business continuity crises.
In the event of a large-scale disaster (earthquake, fire, flood, terrorism) that may interrupt the continuation of core business by site, each plant will avoid suspending the wafer business as much as possible. Even when suspended, we will return to normal operations in a short time and provide customers with stable products and services.
Expectancy Table of Business Continuity Crises
| Office | Head Office, Niigata Plant |
Tokuyama Plant | Sekikawa Plant | Oguni Crystal Center | Tokyo Office | Kyushu Office |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Address | Niigata Prefecture | Yamaguchi Prefecture | Niigata Prefecture | Yamagata Prefecture | Tokyo | Fukuoka Prefecture |
| Earthquake | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Wind damage | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Tsunami | 〇 | 〇 | - | - | 〇 | 〇 |
| Snow damage | 〇 | - | 〇 | 〇 | - | - |
| Fire | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Outbreak/personnel shortage |
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Terrorism | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Stoppage of important equipment | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | - | - |
| Necessary Materials Procurement Not Possible |
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | - | - |
| Cyberattack | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
BCP Response Team
| Team Leader | President |
|---|---|
| Deputy Team Leader | Executive Officer (Plant/Production Engineering Staff) |
| Team members | Selected from executive officers, office managers, general managers, plant chiefs, and group managers |
| Secretariat | Administration Department,General Affairs Group |
Role of Response Team
- Collection and sharing of information on occurrence risks
- Prevention of reoccurrence
- Responding to new occurrence risks
- External transmission of information
- Follow-up on risk response status
Content and timing of emergency contact to customers
In the event of a large-scale natural disaster or other event that affects the supply of products to customers or that causes concern among customers due to media reports, etc., the sales department cooperates with manufacturing bases to inform customers of items such as the situation, damage status, and impact on product delivery. As a general rule, reports will be made at the following times.
| Elapsed time | Contents of report | |
| 1st report | within 24 hours | Damage situation, approximate impact on shipping assumed in worst case conditions. |
| 2nd report | within 48 hours | Reply with shipping plan (outline). Report on damage status of work in process. |
| 3rd report | within 72 hours | Revise shipping plan (details). Provide a summary of the damage situation. |
Surveying the emergency response status of major business partners
We are investigating the emergency response status of our major business partners, and are requesting them to build, maintain, and update their BCP systems.
We will minimize the impact on production due to shortages of production materials and auxiliary parts by promoting transactions with multiple business partners and securing an appropriate amount of inventory.
Survey emergency contacts, plant locations, and supply chains of major business partners
- Manage with supply risk management sheet
Investigate the BCP response status of major business partners
- Construction status of BCP system
- Initial status in an emergency
- Response status in an emergency
- Status of ascertaining risks
- Status of diversifying risks
- Status of disaster prevention development
